前言
尊重原创,本系列文本解析部分主要基于Candidate for Master’s Degree School of Computer Wuhan University的K_Eckel([email protected])《设计模式精解-GoF 23 种设计模式解析附 C++实现源码》。为了避免重造轮子,本系列博文对源码在ubuntu16.04下做了验证并上传到了gitee,再次感谢。
如有问题,可邮件联系我([email protected])并共同探讨解决方案。
目录
创建型模式(Creating Pattern)
Factory 模式 | AbstactFactory 模式 | Singleton 模式 | Builder 模式 | Prototype 模式
结构型模式(Structrual Pattern)
Bridge 模式 | Adapter 模式 | Decorator 模式 | Composite 模式 | Flyweight 模式 | Facade 模式 | Proxy 模式
行为型模式(Behavioral Pattern)
Template 模式 | Strategy 模式 | State 模式 | Observer 模式 | Memento 模式 | Mediator 模式 | Command 模式 | Visitor 模式 | Iterator 模式 | Interpreter 模式 | Chain of Responsibility 模式
Composite 模式简介:
组合模式(Composite Pattern),又叫部分整体模式,是用于把一组相似的对象当作一个单一的对象。组合模式依据树形结构来组合对象,用来表示部分以及整体层次。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它创建了对象组的树形结构。
这种模式创建了一个包含自己对象组的类。该类提供了修改相同对象组的方式。
问题
在开发中,我们经常可能要递归构建树状的组合结构,Composite 模式则提供了很好的解决方案。
模式选择
Composite 模式的典型结构图为:
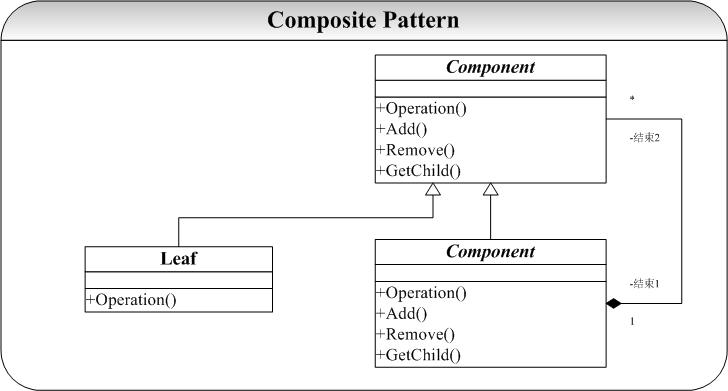
图 1:Composite Pattern 结构图
实现
完整代码示例(code)
Composite 模式的实现起来很简单,这里为了方便初学者的学习和参考,将给出完整的实现代码(所有代码采用 C++实现,并在 Visual Studio Code,Version: 1.36.1 下测试运行)。
源码gitee地址:点击这里
代码目录结构:
patten@patten-hp:~/workspace/others/cpp/designPatterns/structuralPattern/Composite/src$ tree ../
../
├── include
│ ├── Component.h
│ ├── Composite.h
│ └── Leaf.h
└── src
├── Component.cpp
├── Composite.cpp
├── Leaf.cpp
└── main.cpp
2 directories, 7 files
Component.h:
// Component.h
#ifndef _COMPONENT_H_
#define _COMPONENT_H_
class Component {
private:
/* data */
public:
Component(/* args */);
virtual ~Component();
virtual void Operation() = 0;
virtual void Add(const Component&);
virtual void Remove(const Component&);
virtual Component* GetChild(int);
};
#endif //~_COMPONENT_H_
Component.cpp:
//Component.cpp
#include "../include/Component.h"
Component::Component(/* args */) {}
Component::~Component() {}
void Component::Add(const Component& com) {}
Component* Component::GetChild(int index) { return 0; }
void Component::Remove(const Component& com){}
Composite.h:
//Composite.h
#ifndef _COMPOSITE_H_
#define _COMPOSITE_H_
#include "Component.h"
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Composite:public Component
{
private:
vector<Component*> comVec;
public:
Composite();
~Composite();
void Operation();
void Add(Component* com);
void Remove(Component* com);
Component* GetChild(int index);
};
#endif //~_COMPOSITE_H_
Composite.cpp:
// Composite.cpp
#include "../include/Composite.h"
#include "../include/Component.h"
Composite::Composite() { vector<Component*>::iterator itend = comVec.end(); }
Composite::~Composite() {}
void Composite::Operation() {
vector<Component*>::iterator comIter = comVec.begin();
for (; comIter != comVec.end(); comIter++) {
(*comIter)->Operation();
}
}
void Composite::Add(Component* com) { comVec.push_back(com); }
void Composite::Remove(Component* com) {
comVec.pop_back();
}
Component* Composite::GetChild(int index) { return comVec[index]; }
Leaf.h:
//Leaf.h
#ifndef _LEAF_H_
#define _LEAF_H_
#include "Component.h"
class Leaf:public Component
{
private:
/* data */
public:
Leaf(/* args */);
~Leaf();
void Operation();
};
#endif //~_LEAF_H_
Leaf.cpp:
// Leaf.cpp
#include "../include/Leaf.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Leaf::Leaf(/* args */) {}
Leaf::~Leaf() {}
void Leaf::Operation() { printf("Leaf operation..... \n"); }
main.cpp:
// main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "../include/Component.h"
#include "../include/Composite.h"
#include "../include/Leaf.h"
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
Leaf* l = new Leaf();
l->Operation();
Composite* com = new Composite();
com->Add(l);
com->Operation();
Component* ll = com->GetChild(0);
ll->Operation();
return 0;
}
代码说明
Composite 模式在实现中有一个问题就是要提供对于子节点(Leaf)的管理策略,这里使用的是 STL 中的 vector,可以提供其他的实现方式,如数组、链表、Hash 表等。
编译运行结果:
patten@patten-hp:~/workspace/others/cpp/designPatterns/structuralPattern/Composite/src$ g++ *.cpp -std=c++11
patten@patten-hp:~/workspace/others/cpp/designPatterns/structuralPattern/Composite/src$ ./a.out
Leaf operation.....
Leaf operation.....
Leaf operation.....
讨论
Composite 模式通过和 Decorator 模式有着类似的结构图,但是 Composite 模式旨在构造类,而 Decorator 模式重在不生成子类即可给对象添加职责。Decorator 模式重在修饰,而Composite 模式重在表示。



